In a garment factory, the production manager’s day starts with production reports. The production manager enters to the factory floor with questions such as -
- How many garments are made last production day by each line? Compare actual production with the production target given to the floor in-charge and line supervisors.
- What were the issues for low production?
- Why too many quality issues?
- Who is responsible for not achieving yesterday’s target?
In this industry, line supervisors are very smart to tell you numbers to show good line performance and hide their shortfall. So, instead of discussion and verbal reports, most of the managers believe in written and printed reports.
To know the factory’s day-to-day performance very well what all production and production-related reports must be made and reported to higher management? Each factory has its own set of policies and systems to run its factory. So, the list of production reports may vary from company to company.
There are few common reports; those are widely used and are very important to know your business well. In this article, I have listed such reports and explained the purpose of those reports. All reports are related to production. Few reports are information-based and others are analysis and performance-based.
See also: MIS Formats used in Garment Manufacturing
1. Operator Attendance Report:
This report explains how many sewing operators; helpers are present today in each line. From this report managers quickly assess, what would be today’s production target. Which lines have a shortage of operators and where there are enough operators and from where some operators can be shifted to another line to fill all lines and run production smoothly?The operator attendance report is an important one for to floor in-charge. Yesterday’s operator’s clock-in and clock-out report is also important to see whether all operators worked full time or not.
2. Daily Production Report (DPR):
Daily Production Report contains yesterday’s production records line wise and style-wise. Production information in term of –- How many cutting has been loaded to each line yesterday and total loading done to a particular from the loading of the style?
- How many pieces have been stitched yesterday and cumulative production till-date of all styles those are currently loaded.
- How many pieces have been dispatched to finishing or washing department?
- Form daily production report managers can assess, whether a line is producing as per target or production is getting delayed.
 Figure: Daily Production Report. Click on the image to enlarge.
Figure: Daily Production Report. Click on the image to enlarge.3. Hourly Production Report:
This report carries information about today’s hourly production. In this report line’s output is being updated hourly or bi-hourly. This report helps line supervisors to chase operators when the line output goes down. Where production data is recorded manually, only line output data is captured and displayed on the production board. But factories that use a real-time production monitoring system, operator-wise and operation-wise hourly production data can be viewed. I have shown one such report for example in the following image.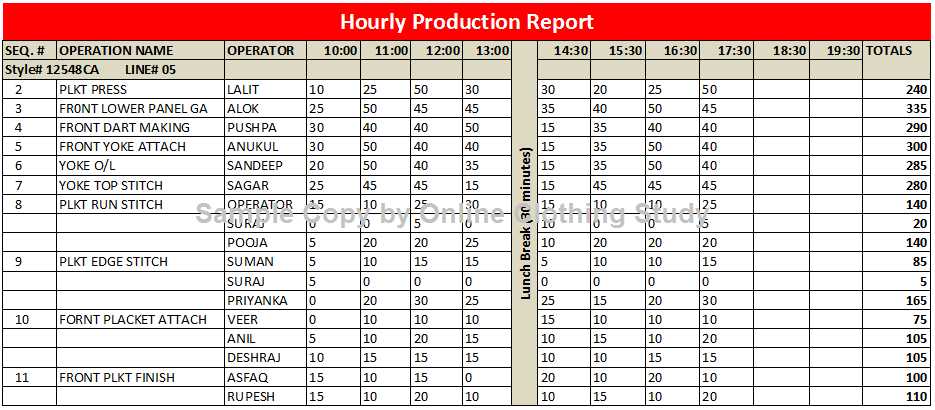 |
| Hourly production Report. Click on the image to enlarge. |
4. Efficiency and Productivity Report:
The daily production report provides actual output numbers of each line and each style. The line output is directly proportional to the number of manpower in a line. If you have two different styles (of different work content) running in two lines, the performance of that line can’t be compared with output figures.The easy way to check the line’s performance is by measuring line efficiency and machine productivity irrespective of styles, manpower utilized or machine used.
5. Manpower and Machine utilization Report:
Manpower and machines are the primary resources of a company. A Manager needs to look into resources to check how company resources are get utilized? The factory should not have excess manpower on the floor. On the other hand, the factory must have the minimum required manpower for a factory to produce goods according to the plan. Both the manpower and machines are the cost to the company. So it is important to check this report daily basis.This report may also include a number of employees who were present during overtime work hours?
