Spinning is the process of conversion of textile fibers and filaments into yarns for weaving or knitting into fabrics. In this article, we are going to know about the various processes which lead to the formation of worsted spun yarns.


Worsted spun yarns differ from the regular woollen yarn in various properties. Only fibers with long staple length (4 inches or longer) are taken for further processing. The yarns are carded and combed thus making them stronger, finer and smoother. Worsted yarns are used mostly for weaving as it is able to withstand the rigorous weaving process and produce smooth woven fabric.
The spinning of worsted spun yarn is carried on through the following process
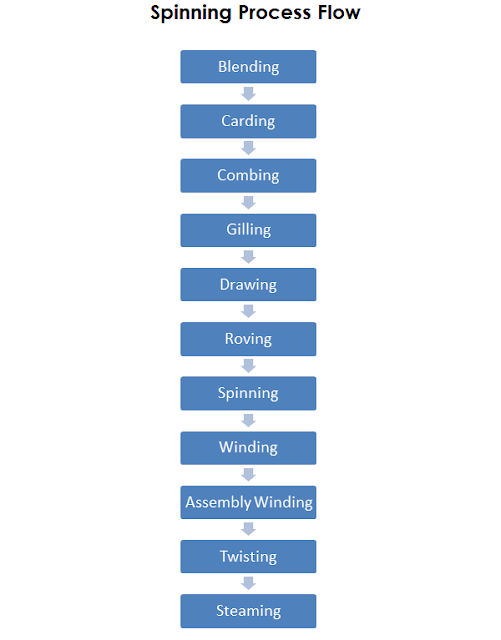 |
| Spinning process flow chart |
Blending
Wool as in raw material comes in the form of a
bale. During blending a number of bales are mixed together to minimize
variations throughout the yarn and thus in the fabric. This homogeneous mixture
also ensures uniformity in the properties of the yarn. It is done by opening up
the bales simultaneously and the fibers are taken over to blending bin where is
loaded onto a reed table which has spike apron fluffs which essentially tears
up through the bales and through compressed air mixes the fibers uniformly.
 |
| Blending machine |
Carding
It is the mechanical process which disentangles,
cleans and intermixes fibers using a series of dividing and redividing steps
that cause the fibers to lie parallel to one another to produce a thin sheet of
uniform thickness of fiber called lay. This lay is then condensed to form a
continuous web of fiber known as a sliver. This marks the beginning of the
spinning process as the slivers will be further drawn to convert it into yarn.
Combing
It separates out the shorter fiber (less than
4inch) by rotating rings or rectilinear row of steel pins. This process is not
required in the woolen system as the short fibers are retained for further
processing. The shorter fibers removed are called noils and are used as a
decorative additive in the further spinning process.
Gilling
The carded wool is then passed through the gilling
and combing operation. Through this process, the shorter fibers are further
removed and the longer fibers (top) are aligned as parallel as possible. It
also helps to remove any impurities left during the carding process. The fibers
aligned in the top produce thus have been straightened and lie parallel to each
other. It also helps in further blending of the fibers and improves uniformity
throughout the bundle.
Drawing
This process can also be done on the gilling machine.
In it, the slivers are further drawn into a more compact form thus making it
thinner for yarn preparation. Only the machine settings are to be changed for the drawing process in the gilling machine. Depending upon requirements of the yarn
one or more drawing process is given in succession.
 |
| Draw frame |
Roving
The purpose of the roving operation is to reduce the
sliver to a suitable size for spinning. The slivers are passed through sets of
rollers with increasing speed. This helps
to further minimize the linear fiber density, preparing it for the
process of spinning. During roving, a small amount of twist is also added which
helps in the drawing of the roving down to the required linear density. The
roving is then rolled upon roving bobbin.
 |
| Roving machine |
Spinning
After roving, the roving bobbin are fed into ring
frame where the roved wool is further drawn out into yarn. During this process
a small amount of twit is added which strengthen the yarn and also helps in the
drawing process. The yarn is then winded onto ring bobbin for further winding.
 |
| Spinning - ring frame |
Winding
The ring spinning bobbins have a small package
size due to the machine limitations. For the further processes, large package
is required for better production rates. If the small ring spun bobbins are
used in the further processes, they would have to be replaced frequently which
would reduce the efficiency of the machine. For this purpose, the Auto coner is
used to make bigger packages from the ring spun bobbins. Along the process yarn
defects like slub, thick and thin places are rectified by cutting and splicing
at that point. In the present day, most of the factories have automatic cutting
and splicing attachments on the autoconer.
 |
| Autoconer machine |
Assembly winding
The strength of a single yarn is always
lesser than that of a double ply yarn. For the process of weaving a warp yarn
requires greater strength which a single ply yarn is insufficient to provide.
By doubling the yarn the strength of the yarn increases many folds. In this
machine, the packages made in the autoconer are used. Two packages are used and
doubled to form one double ply yarn.
Twisting
The double yarn formed in the assembly winding
machine is not twisted. Without the twist, there always remains a chance that
the pry yarns may separate from each other. This is done by TFO(Two For One)
machine where the machine runs between 8000-10500 rpm to provide the suitable
twist needed.
 |
| Twisting |
Steaming
After the process of twisting the wounded yarns
are set for steaming in autoclave machine which is a strongly heated container
used for steam sterilization. With controlled steam and pressure the twist
imparted becomes permanent and then the spool finally gets ready for weaving or
other end uses.
If the fibres need to be dyed then it is done through top
dyeing, but after dyeing the top is to be further passed through gilling and
recombing stages again. This also helps in the blending of the dyed fibers .
Ref: https://nptel.ac.in
